What is probiotics?
Probiotic microorganisms are defined as “live microorganisms, which when consumed in adequate amounts, confer a health effect on the host”. Probiotics have several beneficial health effects and most of these are related to the gastrointestinal system. Probiotics show their benefits via producing inhibitors, the inactivation of pathogens and degradation of carcinogenic and mutagenic compounds.
Probiotics are sensitive microorganisms that high temperatures can cause irreversible changes in the functional integrity of bacterial membranes and proteins and this effect results in the inactivation of probiotics. One of the main challenges in drying of probiotic containing food formulation is to protect the viability of probiotics.
Refractance window drying of probiotics
Refractance window drying is an innovative technique that allows food to be dried at low temperatures and times. Recent studies have showed that refrectance window drying is affective in the protection of probiotics during drying process. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum cells was dried by refractance window dryer in the presence of fructooligosaccharide, whey protein and maltodextrin.
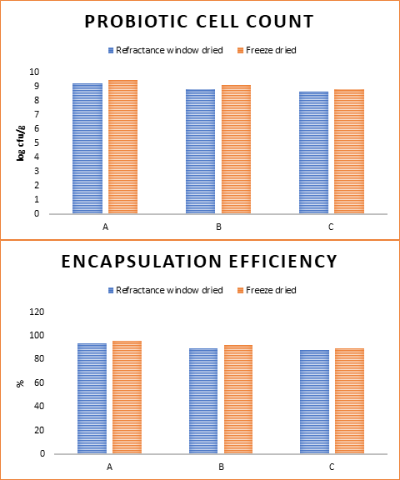
After refractance window drying, the cell count was determined in the level of 9 cfu/g. Additionally, over the 88% cell protection was achived by drying. These results were similar by freeze dried probiotic cells . These results showed that, refractance window drying does not cause probiotic microorganism inactivation when carried at low temperatures On the other hand, in vitro studies revealed that refractance window drying increased the stability of probiotics during gastric passage (Yoha et al., 2019).
Need mor information about our technology, you can read Refractance Window Drying Technology post.
Interested in our dryers, get more information on our services page.
References
K. S. Yoha, J. A. Moses & C. Anandharamakrishnan (2019): Conductive hydro drying through refractance window drying – An alternative technique for drying of Lactobacillus plantarum (NCIM 2083), Drying Technology, DOI: 10.1080/07373937.2019.1624972